All You Need To Know About Web Designers [Infographic]
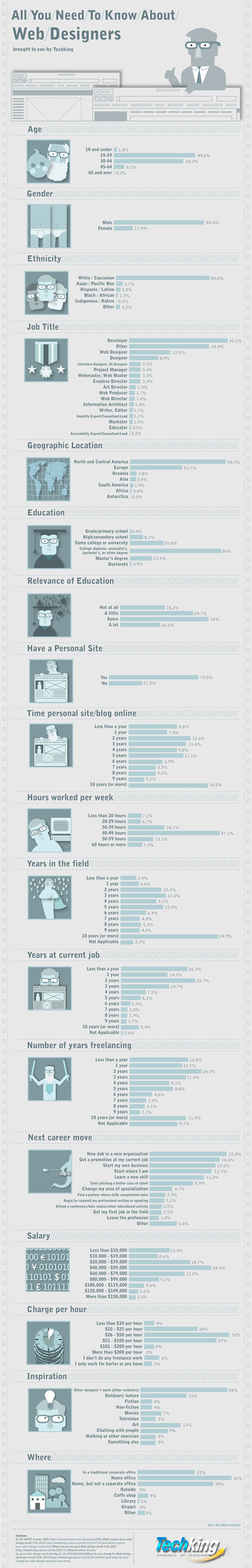
Today we have a special edition of our infographic series – a huge roundup of facts and figures about our fellow web designers. Learn everything you need to know (and more) about web workers from a single glance. For this graphic we used the following sources: A List Apart Survey, 2009, What inspires your web design work? Poll, 2010, Where do you do your Web design work? Poll, 2007 & What do you charge for Web design work (per hour)? Poll, 2010. Click here to get the full size version!
Web designers must possess an innate understanding of visual hierarchy, color theory, typography, and spatial relationships that guide user attention and create engaging digital experiences. These professionals craft layouts that balance aesthetic appeal with functional usability, ensuring every element serves a purpose while contributing to overall design harmony. Successful web designers study composition principles derived from traditional art forms while adapting them for digital mediums with unique constraints and opportunities. They recognize that effective design transcends personal preference, grounding decisions in user research, accessibility standards, and conversion optimization principles. Mastering visual design fundamentals enables designers to create interfaces that communicate brand identity, establish credibility, and guide users toward desired actions through strategic placement of content and interactive elements.
The discipline requires continuous refinement as design trends evolve and user expectations shift with technological advancement. Modern web designers must balance contemporary aesthetics with timeless design principles that ensure longevity beyond fleeting trends. They develop sensitivity to negative space, understanding how empty areas provide visual breathing room that prevents overwhelming users with excessive information. Typography selection influences readability and brand personality, with designers choosing typefaces that align with content tone and audience preferences. Color palettes establish emotional resonance and visual consistency across pages, while contrast ratios ensure text remains legible for users with visual impairments. For designers seeking to enhance navigation experiences, exploring techniques for hiding scroll bars effectively demonstrates how subtle interface refinements improve overall user experience.
Interactive Elements and User Engagement Strategies
These professionals understand that static layouts fail to capture attention in competitive digital environments where users expect dynamic, responsive interfaces. Effective interaction design provides visual confirmation of user actions, reduces perceived wait times through loading animations, and guides attention toward important content through subtle motion. Designers balance interactivity with performance, ensuring animations enhance rather than hinder usability through excessive file sizes or distracting movements. They apply principles of microinteractions that provide delightful moments throughout user journeys, transforming mundane tasks into memorable experiences that differentiate brands from competitors. Contemporary web designers leverage CSS animations, JavaScript libraries, and modern frameworks to implement sophisticated interactions without compromising page load speeds.
They prototype interactions early in design processes, testing how users respond to various animation timings, easing functions, and trigger mechanisms. Accessibility considerations ensure interactive elements remain usable for keyboard navigation and screen reader users who cannot rely on visual cues alone. Performance monitoring identifies interactions that tax processor resources, prompting optimization or simplification to maintain smooth experiences across device capabilities. For technical implementation details, understanding how assignment operators manage values in programming languages helps designers communicate effectively with development teams about state management in interactive components.
Responsive Design and Multi-Device Optimization
Web designers in contemporary practice must create fluid layouts that adapt seamlessly across smartphones, tablets, desktop monitors, and emerging form factors like foldable screens and wearable devices. Responsive design transcends simply shrinking content to fit smaller screens, requiring thoughtful reorganization of information hierarchies, navigation patterns, and interactive elements optimized for touch and gesture interfaces. These professionals employ flexible grid systems, proportion-based sizing, and breakpoint strategies that maintain design integrity across viewport dimensions. Design systems and component libraries facilitate consistent responsive behaviors across projects, with reusable patterns ensuring predictable adaptation across breakpoints.
Designers specify flexible image sizing, font scaling, and spacing adjustments that maintain proportional relationships regardless of screen dimensions. They consider context differences between device types, recognizing that mobile users often seek quick information while desktop users might engage in deeper content exploration. Performance optimization becomes crucial for mobile experiences where network speeds and processing power may be limited compared to desktop environments. Those interested in how computational workloads distribute across infrastructure should explore edge computing paradigms that parallel responsive design’s principle of optimizing experiences for specific contexts.
Collaboration Tools and Remote Work Methodologies
Modern web design increasingly occurs within distributed teams using specialized collaboration platforms that facilitate real-time communication, file sharing, version control, and project management. Designers must master tools that enable asynchronous collaboration across time zones while maintaining design consistency and project momentum. These professionals document design decisions, create detailed style guides, and establish component libraries that enable team members to implement designs accurately without constant designer oversight. They participate in video conferences for stakeholder presentations, conduct remote user testing sessions, and provide design feedback through annotated screenshots and screen recordings. Effective collaboration requires clear communication skills that translate visual concepts into written descriptions when face-to-face discussion is impossible.
Cloud-based design tools have revolutionized team workflows by eliminating file versioning conflicts and enabling simultaneous editing of design files. Designers share prototypes through URLs that stakeholders access without installing specialized software, lowering barriers to feedback collection. Integration between design tools and project management platforms creates automated workflows that notify developers when assets are ready for implementation. Time zone differences require asynchronous communication patterns documented through written comments, recorded video explanations, and comprehensive documentation that team members reference independently. For teams seeking streamlined communication, platforms like Slack enable seamless collaboration through channels, direct messaging, and integration with other productivity tools.
Prototyping Workflows and Iterative Design Processes
Low-fidelity wireframes establish information architecture and layout structures without visual design distractions. Mid-fidelity mockups introduce typography, color schemes, and realistic content while maintaining rapid iteration capabilities. High-fidelity prototypes simulate final interfaces with accurate interactions, animations, and content that stakeholders experience as nearly complete products. Designers select appropriate fidelity levels based on project phase, recognizing that excessive polish in early stages wastes effort on concepts that may require fundamental restructuring. Prototyping tools range from simple sketching applications to sophisticated platforms offering conditional logic, variable management, and user testing capabilities.
Interactive prototypes enable usability testing that reveals navigation confusion, unclear labeling, and interaction patterns that fail to match user mental models. Designers observe users attempting tasks within prototypes, identifying friction points that quantitative analytics alone might miss. Iteration cycles incorporate feedback from stakeholders, users, and development teams who identify technical constraints requiring design adjustments. Version control within prototyping tools preserves design history, enabling comparison between iterations and reversion to previous concepts when new directions prove unsuccessful. Balancing thoroughness with efficiency becomes crucial, as professionals must recognize when speed and quality require balance rather than pursuing perfection that delays market entry.
Accessibility Standards and Inclusive Design Practices
They implement semantic HTML that conveys content structure to assistive technologies, provide alternative text for images, ensure sufficient color contrast for low vision users, and create keyboard navigation paths for those unable to use pointing devices. Accessibility guidelines like WCAG provide measurable criteria for evaluating design decisions against established standards. These professionals recognize that accessible design benefits all users, not just those with disabilities, as features like captions assist users in sound-sensitive environments and keyboard shortcuts accelerate power user workflows. Legal compliance motivates accessibility in many jurisdictions, but ethical design centers user needs regardless of regulatory requirements.
Inclusive design extends beyond disability accommodation to consider cultural differences, language preferences, connectivity limitations, and device capabilities that affect how diverse audiences experience digital products. Designers test interfaces with screen readers, keyboard-only navigation, and browser zoom features to identify barriers that prevent equitable access. They specify focus indicators, skip navigation links, and ARIA labels that enhance experiences for assistive technology users. Color cannot serve as the sole method of conveying information, as colorblind users cannot distinguish certain hue combinations. Form design includes clear labels, error messages, and input validation that assists all users in completing tasks successfully. For developers implementing accessible interfaces, understanding how JavaScript handles object identification ensures proper DOM manipulation maintains accessibility.
Performance Optimization and Load Time Reduction
Web designers directly influence site performance through decisions about image formats, file sizes, font loading strategies, and third-party script integration. Performance impacts user satisfaction, search engine rankings, and conversion rates, making optimization a core design responsibility rather than solely technical concern. These professionals compress images without perceptible quality loss, select modern formats like WebP that offer superior compression, and implement responsive image techniques that serve appropriately sized files based on device capabilities. They minimize web font usage, subset font files to include only required characters, and specify font-display properties that prevent invisible text during loading. Critical rendering path optimization ensures above-the-fold content loads quickly, with non-essential elements deferred until after initial page rendering.
Third-party scripts for analytics, advertising, and social media integration often represent the largest performance bottlenecks, requiring designers to balance functionality against speed. They specify lazy loading for images and videos below the fold, preventing unnecessary downloads until users scroll toward content. Design decisions about carousel implementations, parallax effects, and animated backgrounds directly impact JavaScript execution time and rendering performance. Designers collaborate with developers to establish performance budgets that quantify acceptable file sizes and load times, informing design choices throughout projects. Understanding how value stream mapping identifies inefficiencies helps designers optimize workflows that contribute to faster delivery and better performance outcomes.
Content Strategy and Information Architecture
Effective web design requires organizing information logically through clear navigation systems, intuitive categorization, and content hierarchies that help users find desired information efficiently. Designers collaborate with content strategists to determine appropriate information architecture based on user research, card sorting exercises, and analytics revealing common user paths. They create sitemaps visualizing site structure, wireframes establishing page-level organization, and navigation schemes that balance discoverability with simplicity. Search functionality becomes essential for content-rich sites where navigation alone cannot efficiently surface all available information. Breadcrumb trails help users understand their location within site hierarchies, while related content links encourage exploration beyond initial landing pages.
Content presentation influences how users consume information, with designers specifying appropriate line lengths, paragraph spacing, and heading hierarchies that enhance readability. They integrate media strategically, using images, videos, and infographics to clarify complex concepts and break up text-heavy pages. Call-to-action placement guides users toward conversion goals, with visual prominence reflecting business priorities. Progressive disclosure reveals complex information gradually, preventing overwhelming users with excessive detail upfront while providing depth for those seeking comprehensive information. For technical content, techniques like string splitting in Python demonstrate how developers manipulate data structures, paralleling how designers structure information for optimal comprehension.
Design Systems and Component Libraries
Mature web design practices emphasize reusable components and systematic design approaches that ensure consistency across products while accelerating design and development workflows. Design systems document color palettes, typography scales, spacing units, and component behaviors that team members reference when creating new interfaces. These living documents evolve with products, capturing design decisions and rationales that prevent duplicate effort and maintain coherent brand expression. Component libraries provide pre-designed, pre-coded elements like buttons, form fields, cards, and modals that designers and developers leverage rather than creating from scratch. Atomic design methodologies organize components hierarchically from basic elements through complex organisms, facilitating reuse and systematic thinking.
Design tokens abstract design values into platform-agnostic variables that translate into platform-specific implementations, enabling consistent designs across web, iOS, Android, and other platforms. Governance processes define who can contribute to design systems, approval workflows for new components, and deprecation strategies for outdated patterns. Documentation includes usage guidelines, accessibility specifications, and code snippets that reduce implementation ambiguity. Design system adoption requires cultural change where team members embrace constraints that ensure consistency over unlimited creative freedom. Understanding programming concepts strict aliasing in C highlights how technical constraints guide correct implementation, similar to how design systems provide guardrails for consistent interfaces.
Data Visualization and Information Graphics
Web designers working with data-rich applications must translate complex datasets into visual representations that reveal patterns, trends, and insights accessible to non-technical audiences. They select appropriate chart types based on data characteristics and communication goals, understanding when bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, heat maps, or custom visualizations best serve analytical purposes. Color usage in data visualization requires careful consideration of accessibility, ensuring colorblind users can distinguish categories through patterns or labels beyond hue alone. Interactivity enables exploration of multidimensional data through filtering, zooming, and detail-on-demand techniques that balance overview comprehension with granular analysis. These professionals balance aesthetic sophistication with clarity, recognizing that overly decorative visualizations obscure rather than illuminate underlying data.
Dashboard design organizes multiple visualizations into coherent interfaces that support monitoring and decision-making workflows. Designers establish visual hierarchies that prioritize critical metrics while providing access to supporting details. Real-time data visualization presents unique challenges around update frequencies, transition animations, and state management that prevent disorienting users with constant changes. Responsive data visualization adapts chart dimensions and complexity levels based on available screen space, sometimes switching chart types between mobile and desktop contexts. For those interested in analytical tools, exploring why R language serves analysts provides insights into statistical computing environments that produce visualizations designers might incorporate into web interfaces.
Career Progression and Compensation Trends
Web design careers follow various trajectories from junior designers learning fundamentals through senior designers leading projects and principal designers shaping organizational design strategies. Specialization opportunities include user experience design, user interface design, motion design, design systems architecture, and design leadership roles. Compensation varies significantly based on experience, location, industry, and specialization, with designers in major technology hubs and specialized roles commanding premium salaries. Junior designers typically earn entry-level salaries while building portfolios and developing skills, with rapid compensation growth as they demonstrate impact through successful projects. Mid-level designers take increasing responsibility for project outcomes, mentor junior team members, and contribute to design strategy beyond execution tasks.
Senior designers often move into management tracks overseeing design teams or principal individual contributor tracks influencing product direction and establishing design culture. Continuous learning remains essential as design tools, technologies, and best practices evolve rapidly. Designers invest in conference attendance, online courses, industry publications, and experimental projects that expand capabilities beyond daily work requirements. Portfolio quality significantly influences hiring and advancement opportunities, with designers curating projects that demonstrate problem-solving approaches, collaboration skills, and measurable impact rather than solely aesthetic execution. Those curious about compensation in related fields might explore data scientist earnings which share similar analytical and technical skill requirements with specialized design roles.
File Management and Asset Organization
Professional web designers maintain organized file structures that enable efficient collaboration, version control, and asset handoff to development teams. Naming conventions ensure files are self-documenting, with descriptive names that convey content, version, and status without requiring external documentation. Folder hierarchies separate source files from exported assets, organize components by type or page, and maintain archives of previous versions for reference or reversion. Cloud storage solutions enable access from multiple devices and locations while facilitating sharing with team members and stakeholders. Regular backups protect against data loss from hardware failures, accidental deletions, or corrupted files that could compromise project deliverables.
Asset management extends to organizing design system components, icon libraries, image collections, and stock assets licensed for projects. Metadata tagging enables efficient searching within large asset collections where folder organization alone proves insufficient. Version control systems track changes to design files, enabling comparison between iterations and collaborative editing without file conflicts. Export automation streamlines asset preparation for development, generating optimized image files at required dimensions and formats without manual processing. Understanding technical aspects like proper file closing in Python demonstrates attention to detail in resource management that parallels designers’ asset organization responsibilities.
Security Considerations in Design Implementation
Web designers increasingly consider security implications of design decisions, particularly around user authentication, payment processing, and personal data collection. They design clear password requirements that balance security with usability, avoiding overly complex rules that encourage insecure workarounds. Two-factor authentication interfaces guide users through additional verification steps without creating excessive friction. Payment form design builds user confidence through security indicators, clear privacy policies, and brand trust signals that reduce cart abandonment. Designers avoid storing or displaying sensitive information unnecessarily, following data minimization principles that limit exposure risks. Error messages provide helpful guidance without revealing system details that could assist attackers.
HTTPS indicators and security badges reassure users about data protection, though designers recognize these elements alone cannot guarantee security without proper technical implementation. Cookie consent interfaces comply with privacy regulations while respecting user attention and comprehension limits. Password visibility toggles balance security with usability for users who struggle with masked input fields. Automatic logout timers protect against unauthorized access on shared devices, with designers specifying appropriate timeout durations and clear warnings before sessions expire. For technical implementation details, exploring serverless security best practices demonstrates how security permeates all aspects of modern web development.
Professional Certifications and Skill Validation
While web design lacks universal professional licensing, various certifications demonstrate proficiency in specific tools, methodologies, or specialized domains. Platform-specific certifications from Adobe, Sketch, Figma, and other tool vendors validate technical proficiency in industry-standard applications. Accessibility certifications demonstrate commitment to inclusive design practices and knowledge of WCAG guidelines. User experience certifications from Nielsen Norman Group, Interaction Design Foundation, and universities provide structured learning paths and credential recognition. These certifications complement practical experience and portfolio quality rather than substituting for demonstrated capabilities. Employers vary in how they value certifications, with some viewing them as valuable validation and others prioritizing portfolios and work samples.
Continuing education maintains relevance as design practices evolve, with designers pursuing online courses, workshops, and self-directed learning to expand capabilities. Industry conferences provide networking opportunities, exposure to emerging trends, and inspiration from peer presentations. Design communities offer feedback on work-in-progress projects, job opportunities, and collective knowledge sharing. Mentorship relationships accelerate skill development through guidance from experienced practitioners who provide context beyond what courses teach. For networking professionals seeking advancement, exploring Cisco CCNP specializations demonstrates how certifications structure professional development in adjacent technical fields.
Network Architecture and Connectivity Foundations
Web designers benefit from basic networking knowledge that informs performance optimization, security considerations, and troubleshooting capabilities. Understanding how DNS resolves domain names to IP addresses helps designers appreciate why hosting choices affect global performance. Content delivery networks distribute assets geographically, reducing latency for users far from origin servers. HTTP protocols define how browsers request resources and servers respond, with HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 offering performance improvements through multiplexing and reduced overhead. SSL/TLS encryption protects data in transit, with designers specifying HTTPS for all pages particularly those handling sensitive information.
API integration enables dynamic content and third-party service incorporation, with designers collaborating with developers to understand data flow and response handling. WebSockets enable real-time bidirectional communication for features like chat, collaborative editing, and live updates. Caching strategies reduce server load and improve perceived performance by storing frequently accessed resources locally. Understanding these networking fundamentals enables more informed design decisions and productive collaboration with technical team members. For deeper networking knowledge, exploring critical network protocols provides insights into communication standards underlying web interactions.
Intrusion Prevention and Security Awareness
Designers contribute to security through awareness of common attack vectors and design decisions that mitigate risks. Cross-site scripting prevention requires properly escaping user-generated content displayed in interfaces, with designers specifying where such content appears. SQL injection risks inform form design where user input could be manipulated if not properly sanitized by backend systems. Clickjacking prevention involves designing clear user consent interfaces that cannot be overlaid maliciously on other sites. CSRF token inclusion in forms protects against unauthorized action submission, though implementation remains primarily technical rather than design concern. Designers avoid creating interfaces that encourage risky behaviors like sharing credentials or clicking suspicious links.
Security awareness training helps designers recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and suspicious communications that could compromise projects or organizational systems. Regular software updates and strong authentication practices protect design tools and file repositories from unauthorized access. Secure communication channels ensure confidential client information and unreleased designs don’t leak through insecure email or messaging platforms. Understanding security principles enables designers to identify potential vulnerabilities during design phases when fixes cost less than post-deployment remediation. Learning about intrusion detection systems provides context for how security professionals protect the systems designers create interfaces for.
Cloud Platform Integration and Modern Deployment
Contemporary web design increasingly targets cloud-hosted platforms offering scalability, reliability, and integrated services that traditional hosting cannot match. Designers collaborate with cloud architects to understand deployment environments, CDN configurations, and serverless architectures that influence design constraints and opportunities. Platform-as-a-service offerings abstract infrastructure management, enabling designers to focus on user experience while developers handle technical implementation details. Cloud storage services host media assets with designers specifying caching policies and access patterns optimizing performance. Content management systems increasingly deploy on cloud infrastructure, with designers creating themes and templates compatible with cloud-native architectures.
Serverless functions enable dynamic functionality without maintaining dedicated servers, with designers specifying event-driven interactions that trigger backend processing. Cloud-based testing environments enable designers to preview work across different device configurations without maintaining physical device labs. Collaboration tools increasingly run as cloud services accessed through browsers rather than installed applications requiring manual updates and version synchronization. Understanding cloud paradigms enables designers to leverage platform capabilities and collaborate effectively with technical teams. For comprehensive platform knowledge, exploring Microsoft Azure certifications demonstrates structured learning paths for cloud expertise.
Container Orchestration and Deployment Workflows
Modern development and deployment workflows increasingly leverage containerization technologies that package applications with their dependencies, ensuring consistent behavior across development, staging, and production environments. Designers working closely with development teams encounter container concepts when discussing local development environments, deployment processes, and troubleshooting issues across environments. Container orchestration platforms manage deployment at scale, automatically handling load balancing, scaling, and recovery from failures. These technologies enable rapid iteration cycles where design changes deploy quickly without lengthy manual configuration processes. Designers benefit from understanding these technical foundations when discussing timeline expectations and deployment constraints.
Microservices architectures decompose applications into independently deployable services, sometimes requiring designers to create interfaces that integrate across multiple backend services. API contracts define how frontend interfaces interact with backend services, with designers and developers collaborating to ensure designs align with technical capabilities and constraints. Continuous integration and continuous deployment pipelines automate testing and deployment, enabling rapid iteration that supports agile design processes. Understanding deployment workflows helps designers anticipate lead times between design completion and production deployment. For those interested in orchestration platforms, exploring why Kubernetes proves essential demonstrates how container management enables modern application architectures.
Professional Development Through Microsoft Certifications
While web design primarily centers on creative and user experience skills, technical certifications in platforms like Microsoft Azure, Microsoft 365, and development frameworks complement design capabilities. These credentials demonstrate technical depth that enhances collaboration with engineering teams and enables designers to implement certain features independently. Certification paths provide structured learning covering best practices, platform capabilities, and implementation patterns that inform design decisions. Organizations value designers who understand technical constraints and opportunities, enabling more realistic designs that leverage platform strengths. Microsoft certifications in particular span diverse domains from cloud infrastructure through data platforms to security and compliance.
Technical knowledge empowers designers to prototype functional experiences beyond static mockups, creating working implementations that more accurately represent final user experiences. Understanding development frameworks and constraints reduces back-and-forth cycles where designs require modification due to technical limitations discovered during implementation. Full-stack designers who combine visual design skills with coding capabilities command premium compensation and enjoy greater autonomy in bringing concepts to completion. Continuing technical education maintains relevance as platforms evolve and new capabilities emerge. For career acceleration insights, exploring how to advance IT careers with Microsoft certification demonstrates value of structured learning paths.
Cloud Project Selection and Portfolio Development
Web designers strengthening their portfolios benefit from selecting projects that demonstrate diverse skills, problem-solving approaches, and measurable impact rather than solely aesthetic execution. Personal projects allow experimentation with emerging technologies, design trends, and unconventional approaches that client work might not permit. Open-source contributions demonstrate collaboration skills and commitment to community while building public portfolios visible to potential employers. Cloud-based projects showcase understanding of modern deployment models, scalability considerations, and platform integration beyond traditional website design. Designers document project contexts, challenges encountered, and solutions implemented, telling stories that reveal thinking processes beyond final visual outputs.
Case studies articulate design decisions, research conducted, constraints navigated, and outcomes achieved, helping portfolio reviewers understand designer capabilities beyond surface aesthetics. Metrics and testimonials validate impact claims, though designers must balance quantitative results with qualitative improvements to user experience. Portfolio presentation itself demonstrates design capabilities through thoughtful organization, responsive implementation, and attention to details that reflect professional standards. Regular portfolio updates ensure current work remains prominent while archiving outdated projects that no longer represent current capabilities. For project selection guidance, exploring recommendations on choosing Azure projects provides frameworks applicable across technology domains.
Enterprise Software and Complex Interface Design
Enterprise web design addresses unique challenges including complex workflows, dense information displays, power user efficiency requirements, and integration across multiple business systems. These designers create interfaces for customer relationship management, enterprise resource planning, supply chain management, and other specialized business applications. Unlike consumer-facing websites prioritizing simplicity, enterprise applications balance accessibility for occasional users with advanced features serving daily power users. Information architecture becomes particularly complex when organizing dozens or hundreds of features across multiple user roles with varying permissions and responsibilities.
Designers employ progressive disclosure, contextual help, and customizable dashboards that accommodate diverse user needs without overwhelming anyone with irrelevant functionality. Enterprise design systems maintain consistency across product suites while enabling customization for specific client implementations. Designers specify keyboard shortcuts, batch operations, and workflow automation that accelerate repetitive tasks for frequent users. Data-dense tables require thoughtful design balancing compact display with readability, often incorporating filtering, sorting, and column customization enabling users to tailor views. Integration with legacy systems introduces technical constraints that designers navigate while modernizing interfaces incrementally. For organizations seeking comprehensive expertise, exploring IBM certification programs demonstrates how enterprise technology vendors structure professional development for their platforms.
Healthcare Applications and Compliance Requirements
Healthcare web design operates under strict regulatory frameworks including HIPAA in the United States that govern patient data privacy and security. Designers create electronic health record interfaces, patient portals, telemedicine platforms, and medical device software requiring specialized domain knowledge. These applications balance clinical efficiency with patient safety, recognizing that poor interface design can contribute to medical errors with life-threatening consequences. Information display must accommodate high-stakes decision-making under time pressure, with critical information prominently visible and potential drug interactions clearly flagged. Accessibility becomes particularly important given diverse patient populations including elderly users, those with disabilities, and individuals with varying technology literacy.
Audit trails document all data access and modifications supporting compliance verification and incident investigation. Consent management interfaces ensure patients understand how their health information will be used and shared. Secure messaging enables patient-provider communication while maintaining confidentiality. Mobile optimization accommodates both patients accessing portals from smartphones and clinicians using tablets during patient encounters. Healthcare design demands exceptional attention to detail and thorough testing given potential impact of interface failures. Professionals serving regulated industries might explore ICF certifications demonstrating specialized compliance knowledge.
E-commerce Platforms and Conversion Optimization
E-commerce design focuses intensely on conversion optimization, removing friction from purchase paths while building trust that encourages transactions with unfamiliar vendors. Designers optimize product pages showcasing merchandise through high-quality imagery, detailed specifications, customer reviews, and clear calls-to-action. Shopping cart interfaces maintain context about selected items while enabling quantity adjustments and promotional code application. Checkout flows minimize required fields, offer guest checkout options, and clearly display total costs including shipping and taxes before final confirmation. Trust signals including security badges, return policies, and customer service contact information reduce abandonment from security concerns or uncertainty.
Personalization engines recommend products based on browsing history, purchase patterns, and similar customer behaviors, requiring interfaces that present suggestions naturally without appearing invasive. Mobile commerce demands streamlined experiences accommodating small screens and touch interactions without sacrificing functionality. Performance optimization becomes critical as load time delays directly correlate with lost revenue. A/B testing validates design hypotheses through controlled experiments comparing conversion rates across interface variations. E-commerce designers balance business goals around average order value and conversion rate with user experience quality that builds long-term customer relationships. For technical implementation aspects, exploring IFPUG certifications demonstrates function point analysis methods for sizing software projects.
Educational Technology and Learning Management Systems
Educational web design creates engaging learning experiences through interactive content, progress tracking, collaborative features, and adaptive pathways responding to individual learner needs. These designers structure course content into logical sequences balancing instructor-led progression with self-paced exploration. Assessment interfaces accommodate diverse question types including multiple choice, short answer, essays, and interactive simulations requiring specialized input methods. Gradebooks present performance data to students and instructors through visualizations revealing progress and areas needing improvement. Discussion forums facilitate peer interaction and community building that enhances learning beyond isolated content consumption.
Accessibility assumes particular importance given legal requirements that educational institutions provide equal access to students with disabilities. Mobile access enables learning during commutes and spare moments, though designers recognize limitations of small screens for complex content. Gamification elements including badges, points, and leaderboards motivate engagement though designers must avoid trivializing serious learning objectives. Integration with student information systems enables single sign-on and roster synchronization reducing administrative overhead. Educational designers collaborate with instructional designers to translate pedagogical strategies into effective digital experiences. Those interested in certification testing platforms might explore EXIN certifications demonstrating IT service management knowledge.
Financial Services and Trading Platform Interfaces
Financial web design demands real-time data display, transaction security, regulatory compliance, and interfaces supporting complex decision-making under time pressure. Trading platforms present market data through charts, order books, and watchlists enabling rapid analysis and execution. Account management interfaces provide comprehensive portfolio views, transaction histories, and performance analytics helping users track investments. Advisory tools suggest asset allocation strategies, rebalancing opportunities, and tax optimization tactics based on individual circumstances. Security features including multi-factor authentication, session timeouts, and transaction confirmation workflows protect against unauthorized access and accidental errors.
Regulatory disclosure requirements mandate clear communication of fees, risks, and terms through interfaces that users must acknowledge understanding. Real-time alerts notify users of significant account activity, market movements, or margin calls requiring immediate attention. Mobile trading requires careful balance between feature accessibility and prevention of hasty decisions from insufficient analysis. Data visualization transforms complex financial information into comprehensible charts revealing trends and relationships. Financial designers maintain current knowledge of regulatory requirements and industry best practices that inform compliant, user-friendly experiences. For related certifications, exploring IT service management credentials demonstrates frameworks applicable across industries including finance.
Government and Public Sector Digital Services
Government web design prioritizes accessibility, transparency, multilingual support, and service delivery for diverse populations including digitally excluded citizens. These designers create interfaces for benefit applications, license renewals, public records access, and civic engagement platforms. Plain language and clear visual communication help users with varying education levels understand complex government processes and requirements. Accessibility compliance extends beyond WCAG to encompass Section 508 requirements in the United States and similar standards internationally. Multilingual support accommodates diverse populations, though designers recognize translation involves cultural adaptation beyond literal word substitution.
Mobile-first design acknowledges that underserved populations increasingly access services primarily through smartphones. Offline functionality accommodates users with unreliable internet connectivity. Transparency requirements expose government operations through open data portals and public comment interfaces. Security measures protect sensitive citizen information while authentication systems balance security with accessibility for populations lacking traditional identity documents. Government designers navigate bureaucratic constraints and procurement processes that may slow iteration compared to private sector projects. Those interested in service integration might explore IT service management certifications covering service delivery frameworks.
Media and Publishing Platform Experiences
Media web design optimizes content consumption through typography, layout, and reading experiences that keep audiences engaged while supporting advertising and subscription business models. Article layouts balance readability with advertising placement, avoiding intrusive formats that degrade user experience. Typography selection and sizing consider long-form reading comfort across devices. Multimedia integration incorporates video, audio, and interactive graphics enhancing storytelling without overwhelming text narratives. Subscription flows convert casual readers into paying members through compelling value propositions and frictionless conversion paths. Paywalls balance content access with revenue generation, often offering metered systems or preview paragraphs before requiring subscription.
Personalization engines recommend articles based on reading history and interests, increasing engagement and time on site. Social sharing optimizations encourage audience growth through viral distribution. Comment systems foster community while requiring moderation tools that manage uncivil discourse. Newsletter subscription interfaces grow email audiences that provide direct reader relationships. Performance optimization ensures articles load quickly despite rich media inclusion. Media designers balance editorial integrity with commercial imperatives, protecting journalistic content from excessive advertising intrusion. Professionals supporting media infrastructure might review hybrid IT solutions architecture demonstrating modern publishing technology stacks.
Travel and Hospitality Booking Systems
Travel web design facilitates complex research and booking workflows spanning flights, accommodations, rental cars, and activities across multiple providers. Search interfaces accommodate flexible date ranges, destination exploration, and filtering across numerous attributes including price, amenities, and user ratings. Results presentation balances information density with decision-making clarity through thoughtful layout and visual hierarchy. Comparison features enable side-by-side evaluation of options across key criteria. Interactive maps visualize locations relative to points of interest and transportation hubs. Booking flows collect traveler information, payment details, and preferences while minimizing friction that contributes to abandonment before completion.
Personalization leverages past bookings and browsing behavior to suggest relevant destinations and properties. Mobile optimization acknowledges travelers often research and book on smartphones, particularly for last-minute needs. Trip management interfaces consolidate confirmations, itineraries, and change options in accessible formats. Loyalty program integration rewards frequent customers while encouraging direct book ings rather than third-party channels. Travel designers address international audiences through currency conversion, language translation, and cultural adaptations that respect local customs and expectations. Those supporting travel infrastructure might explore server solutions architecture certifications for scalable booking platforms.
Non-Profit and Advocacy Campaign Interfaces
Non-profit web design prioritizes storytelling, donor conversion, volunteer recruitment, and mission communication on often limited budgets. These designers create emotional connections through compelling narratives, impactful imagery, and clear articulation of organizational impact. Donation flows minimize friction through streamlined forms, multiple payment options, and recurring contribution setup. Transparency about fund usage builds donor trust through impact reports and financial accountability. Volunteer recruitment interfaces match interested individuals with opportunities aligned to their skills, availability, and geographic location. Advocacy campaigns mobilize supporters through petition signing, letter writing, and social media amplification requiring one-click participation options.
Event registration systems manage fundraising galas, awareness walks, and community gatherings with ticketing, team formation, and fundraising tracking. Email capture builds mailing lists for ongoing engagement beyond one-time interactions. Mobile optimization recognizes supporters often engage during spare moments on smartphones. Accessibility ensures inclusive participation regardless of ability. Non-profit designers maximize impact within budget constraints through strategic prioritization and leveraging open-source tools. For comprehensive infrastructure knowledge, professionals might explore advanced server solutions architecture certifications.
Real Estate and Property Search Platforms
Real estate web design enables property discovery through sophisticated search, mapping, and comparison tools helping users find ideal homes or commercial spaces. Search interfaces accommodate numerous filters including location, price range, property type, square footage, bedrooms, bathrooms, and amenities. Map integration visualizes property locations relative to schools, transportation, shopping, and other relevant landmarks. Gallery presentations showcase properties through professional photography, virtual tours, and video walkthroughs. Listing details provide comprehensive specifications, neighborhood information, and market context including price history and comparable properties. Contact forms connect interested buyers with listing agents while capturing lead information for follow-up.
Mortgage calculators help users understand affordability and payment scenarios. Saved searches and favorite properties enable users to track interesting listings over time. Alert systems notify users when new properties matching criteria become available. Mobile optimization accommodates users touring neighborhoods and viewing listings on smartphones. Virtual reality integrations provide immersive property tours for remote buyers. Real estate designers balance information density with scannable layouts that support rapid property evaluation. Infrastructure professionals might review hybrid IT architecture credentials for scalable property platforms.
Recruitment and Job Matching Platforms
Recruitment web design connects job seekers with opportunities through profile creation, search, application tracking, and employer branding. Candidate profiles capture work history, skills, education, and preferences in formats that facilitate matching with relevant opportunities. Job search interfaces filter positions by location, industry, experience level, salary range, and work arrangement preferences. Application flows streamline submission through resume parsing, saved information reuse, and integration with professional networking profiles. Employer profiles showcase company culture, benefits, and employee testimonials attracting quality candidates. Application tracking systems help candidates monitor submission status and upcoming interview schedules.
Skill assessments validate candidate capabilities through testing integrated into application workflows. Recommendation engines suggest positions aligned with candidate profiles and browsing behavior. Alert systems notify users about new relevant postings. Mobile optimization accommodates job searching during commutes and breaks. Accessibility ensures inclusive participation in employment opportunities. Recruitment designers balance job seeker needs with employer objectives around qualified candidate attraction. For storage infrastructure supporting large recruitment databases, professionals might explore storage solutions architecture certifications.
Gaming and Entertainment Community Platforms
Gaming web design creates engaging community experiences through forums, leaderboards, tournament organization, and content sharing. User profiles showcase achievements, statistics, and gaming preferences enabling social connections around shared interests. Forum interfaces facilitate discussions about strategies, game updates, and community events. Leaderboard displays rank players globally and among friend groups, fostering competition and achievement. Tournament organization tools manage brackets, scheduling, and results tracking. Content sharing enables players to upload gameplay videos, screenshots, and custom modifications. Live streaming integration connects audiences with content creators broadcasting gameplay.
E-sports coverage provides match schedules, results, and statistics for competitive gaming. In-game integration connects web platforms with gaming clients through APIs sharing progress and enabling cross-platform functionality. Merchandise stores sell branded apparel and accessories to engaged community members. Mobile apps extend community access beyond desktop gaming sessions. Gaming designers create visually striking interfaces matching game aesthetics while maintaining usability across complex features. Infrastructure professionals supporting gaming platforms might review storage solutions for Nimble systems handling massive media libraries.
Automotive and Vehicle Configuration Platforms
Automotive web design enables vehicle research, configuration, dealer location, and purchase initiation through comprehensive digital experiences. Model exploration showcases vehicle lineups through imagery, specifications, and feature comparisons. Configuration tools allow customization of trim levels, colors, options, and accessories with real-time price updates and visual previews. 360-degree vehicle views and interior visualizations help users examine design details. Specification comparisons contrast models across performance, efficiency, safety, and technology features. Inventory search connects users with available vehicles at nearby dealers matching desired configurations. Test drive scheduling integrates calendar availability and location selection.
Trade-in valuation tools estimate current vehicle worth streamlining purchase processes. Payment calculators explore financing and leasing options across different terms and down payments. Dealer locator interfaces find service centers for maintenance and repairs. Owner resources provide manuals, maintenance schedules, and recall information. Mobile apps extend ownership experience through remote vehicle control and monitoring. Automotive designers balance rich visual experiences with performance across varying connectivity. For ethical hacking knowledge protecting automotive platforms, professionals explore certified ethical hacker v11 certification.
Insurance and Financial Protection Platforms
Insurance web design simplifies quote comparison, policy purchase, and claims management across auto, home, life, and commercial coverage. Quote engines collect information about coverage needs and risk factors generating personalized premium estimates. Policy comparison tools contrast coverage levels, deductibles, and exclusions across options. Purchase flows collect detailed information required for underwriting while maintaining momentum toward conversion. Account management interfaces provide policy documents, payment history, and coverage modification options. Claims reporting guides users through incident documentation including photo uploads and witness information. Claims tracking provides status updates throughout adjustment and settlement processes.
Agent locator tools connect users with local representatives for personalized assistance. Educational content helps users understand coverage options and insurance concepts. Mobile optimization enables policy access and claims reporting from incident locations. Document management organizes policies, ID cards, and correspondence in accessible formats. Insurance designers balance information collection requirements with user experience quality. For updated security knowledge protecting financial platforms, professionals explore certified ethical hacker v12 credentials.
Social Networking and Community Building
Social platform design creates spaces for connection, content sharing, and community formation around shared interests or relationships. Profile creation enables self-expression through photos, biographical information, and interest declarations. News feed algorithms surface relevant content from connections and followed pages. Content creation interfaces support text posts, photo albums, videos, and live streaming with varying privacy controls. Reaction mechanisms enable quick engagement beyond detailed comments. Messaging systems facilitate private conversations and group chats. Event organization tools manage invitations, RSVPs, and attendee coordination. Group features create communities around shared interests with moderation tools maintaining healthy discourse.
Privacy controls balance sharing with protection of personal information. Advertisement integration generates revenue while attempting to maintain user experience quality. Mobile apps provide constant connectivity and notification systems keeping users engaged. Accessibility ensures inclusive participation across ability levels. Social platform designers navigate complex challenges balancing engagement optimization with user wellbeing and privacy protection. For current ethical hacking knowledge, professionals review certified ethical hacker v13 certification covering modern security challenges.
Web Application Security Testing and Vulnerability Assessment
Web designers increasingly collaborate with security professionals to ensure interfaces resist common attack vectors and protect user data through defense-in-depth strategies. Security testing identifies vulnerabilities including cross-site scripting, SQL injection, cross-site request forgery, and authentication bypass weaknesses. Designers implement security best practices including input validation, output encoding, and security headers that complement backend protections. Secure authentication interfaces enforce strong password policies, support multi-factor authentication, and protect against brute force attacks through rate limiting. Session management prevents fixation attacks and implements appropriate timeout policies.
Security-conscious designers avoid exposing sensitive information through error messages or unnecessarily verbose logging. Penetration testing validates security controls through authorized simulated attacks revealing weaknesses before malicious actors discover them. Vulnerability scanning identifies outdated components with known security issues requiring updates. Security awareness training helps designers recognize social engineering attempts and phishing targeting project credentials. Incident response planning defines procedures for addressing security breaches including user notification and remediation. Web designers supporting secure applications benefit from understanding application security testing methodologies that identify interface vulnerabilities.
Network Defense and Intrusion Prevention Strategies
Network security encompasses protective measures defending against unauthorized access, data exfiltration, and service disruption through layered defensive controls. Firewalls filter traffic based on source, destination, and protocol allowing legitimate communication while blocking suspicious connections. Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic for attack signatures and anomalous patterns indicating compromise. Intrusion prevention systems actively block detected threats rather than merely alerting administrators. Virtual private networks encrypt communications protecting data traversing untrusted networks. Network segmentation limits lateral movement following initial compromise. Access control lists restrict communication between network zones based on least privilege principles.
Security information and event management systems aggregate logs from diverse sources correlating events to identify complex attack campaigns. Threat intelligence feeds provide indicators of compromise enabling proactive blocking of known malicious infrastructure. Network monitoring establishes behavioral baselines detecting deviations suggesting compromise or policy violations. Designers creating administrative interfaces for security systems prioritize clarity given high-stakes decisions security professionals make based on these tools. Those supporting network defense might explore network defense certifications validating protective capabilities.
Advanced Network Security Architecture and Implementation
Advanced network security combines multiple technologies into comprehensive defense strategies protecting against sophisticated threat actors. Next-generation firewalls inspect application-layer traffic identifying threats that traditional port-based firewalls miss. Sandboxing detonates suspicious files in isolated environments detecting previously unknown malware. Data loss prevention systems monitor outbound traffic preventing sensitive information exfiltration. Email security gateways filter phishing attempts and malicious attachments before reaching users. Web application firewalls protect custom applications from attacks targeting application logic vulnerabilities.
Security orchestration platforms automate incident response coordinating actions across multiple security tools. Zero trust architectures verify every access request regardless of network location eliminating implicit trust based on internal network presence. Microsegmentation creates granular security zones with policy enforcement between segments limiting breach impact. Cloud access security brokers extend security controls to sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services. Deception technologies deploy honeypots and decoys that attract attackers revealing their presence and tactics. Advanced security professionals benefit from updated network defense training covering current threat landscapes.
Application Penetration Testing and Code Review
Application security testing validates that web applications resist exploitation through comprehensive assessment of authentication, authorization, input handling, and session management. Code review identifies security vulnerabilities during development when remediation costs remain minimal compared to post-deployment fixes. Static analysis tools scan source code for common vulnerability patterns without executing applications. Dynamic analysis tools test running applications through automated attack simulations. Manual testing by skilled security professionals identifies complex logic flaws that automated tools miss. Threat modeling identifies potential attack vectors during design phases enabling proactive security controls.
Security requirements define protection objectives that development and design teams must satisfy. Secure coding training helps developers avoid introducing common vulnerabilities during implementation. Security testing integration into continuous integration pipelines prevents vulnerable code from reaching production. Remediation verification ensures fixes actually address identified vulnerabilities without introducing new issues. Designers collaborating on secure applications benefit from understanding application security assessment approaches identifying interface-related vulnerabilities.
Wireless Network Security and Mobile Device Protection
Wireless security addresses unique challenges including shared medium vulnerabilities, eavesdropping risks, and authentication without physical connection. Encryption protocols including WPA3 protect wireless traffic from interception while authenticating authorized devices. Network access control verifies device compliance before granting connectivity. Wireless intrusion prevention detects rogue access points and attacks against wireless infrastructure. VPN usage on untrusted wireless networks protects against local attackers intercepting unencrypted traffic. Mobile device management platforms enforce security policies on smartphones and tablets accessing corporate resources.
Certificate-based authentication strengthens wireless security beyond pre-shared keys vulnerable to compromise. Wireless site surveys identify optimal access point placement while detecting interference sources. Spectrum analysis tools diagnose performance issues and identify unauthorized transmitters. Guest networking provides isolated internet access without exposing internal resources. Location services track device positions supporting asset management and user experience personalization. Web designers creating mobile-first experiences should understand wireless security fundamentals protecting user devices and connections.
Cloud Security Architecture and Compliance Frameworks
Cloud security requires a clear understanding of shared responsibility models that define customer versus provider obligations across infrastructure, platform, and software service models. Identity and access management controls who can access resources by enforcing least-privilege and just-in-time principles that minimize exposure. Encryption safeguards data both at rest and in transit using strong cryptographic standards. Resources such as 512-50 Certification Training reinforce how security groups and network access controls segment cloud resources, limiting lateral movement within environments. Cloud security posture management continuously assesses configurations to identify compliance violations and security weaknesses, while cloud access security brokers provide visibility and control over both sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud service usage.
Security information and event management integrates cloud logs with on-premises systems for comprehensive monitoring. Compliance frameworks including SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and HIPAA mandate specific controls that cloud architectures must satisfy. Data residency requirements govern where information can be stored and processed based on regulatory jurisdictions. Incident response in cloud environments requires understanding provider responsibilities and customer actions during security events. Disaster recovery and business continuity planning leverage cloud availability zones and geographic distribution. Cloud security professionals benefit from cloud security architect certifications validating comprehensive protective expertise.
Enterprise Risk Management and Security Strategy
Chief risk officers oversee comprehensive risk management programs addressing cybersecurity, operational, financial, strategic, and compliance risks. Enterprise risk management frameworks identify, assess, prioritize, and monitor risks across organizations. Risk appetite statements define acceptable risk levels guiding control investment and risk acceptance decisions. Business impact analysis quantifies potential losses from various threat scenarios informing mitigation prioritization. Control frameworks establish systematic approaches to risk reduction through technical, administrative, and physical safeguards. Risk reporting communicates current risk postures to boards and executive leadership enabling informed governance.
Crisis management procedures define organizational responses to major incidents including security breaches, natural disasters, and business disruptions. Business continuity planning ensures critical operations continue during adverse events through redundancy and alternative procedures. Disaster recovery capabilities restore systems and data following disruptions. Insurance transfers certain risks to third parties reducing potential financial impact. Risk culture embeds risk consideration into strategic planning and operational decision-making. Risk professionals benefit from chief risk officer certifications demonstrating comprehensive risk management expertise.
Digital Forensics and Incident Investigation
Digital forensics preserves, analyzes, and presents electronic evidence following security incidents, legal disputes, or policy violations. Forensic imaging creates bit-for-bit copies of storage devices without altering original evidence, while chain of custody documentation tracks evidence handling to ensure admissibility in legal proceedings. Concepts reinforced through resources like EC0-350 Certification Training align closely with file system analysis, which recovers deleted data, establishes file timelines, and identifies critical evidence artifacts. Memory analysis then examines volatile data to capture details about running processes and network connections, and log analysis correlates events across multiple systems to reconstruct attacker actions accurately.
Malware analysis determines capabilities, behaviors, and indicators of compromise for detected threats. Network forensics captures and analyzes traffic revealing communication patterns and data exfiltration. Mobile device forensics extracts data from smartphones and tablets. Cloud forensics addresses challenges of distributed systems and shared infrastructure limiting traditional forensic approaches. Forensic reporting documents findings for technical and legal audiences. Expert testimony presents forensic evidence in legal proceedings. Forensic professionals benefit from computer hacking forensic investigator certifications validating investigation capabilities.
Security Analysis and Vulnerability Management
Security monitoring analyzes logs and alerts from diverse sources identifying potential security events. Malware analysis determines threat capabilities and indicators enabling detection and remediation. Threat intelligence integration provides context about adversary tactics, techniques, and procedures. Incident triage prioritizes response activities based on severity and potential impact. Security operations centers provide continuous monitoring and incident response capabilities. Playbook development standardizes response procedures for common incident types. Automation reduces manual effort in repetitive analysis and response tasks. Metrics demonstrate security operations effectiveness through mean time to detect and respond. Security analysts benefit from security analyst certifications validating analytical and response capabilities.
Security Specialist Roles and Technical Expertise
Security control implementation deploys firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, encryption, and authentication mechanisms. Security testing validates control effectiveness through penetration testing and vulnerability assessment. Security hardening configures systems and applications to reduce attack surface and prevent common exploits. Security research identifies emerging threats and evaluates new defensive technologies. Tool development creates custom security utilities addressing specific organizational needs. Security mentoring shares expertise with less experienced team members building organizational capability. Industry participation through conferences and community engagement maintains current knowledge and professional networks. Security specialists benefit from security specialist certifications demonstrating technical depth in protective technologies.
Industrial Control Systems and Critical Infrastructure Protection
Physical security controls protect against unauthorized facility access and equipment tampering. Change management procedures prevent unauthorized modifications to control system configurations. Vulnerability management addresses security weaknesses while accommodating operational constraints limiting system downtime. Incident response procedures account for safety implications of security events in hazardous environments. Asset inventory maintains accurate records of control system components and configurations. Network segmentation separates control networks from corporate IT systems. Security monitoring detects anomalous behaviors indicating compromise or equipment failure. Vendor management ensures third-party maintenance activities don’t introduce security risks. ICS security professionals benefit from SCADA security certifications validating operational technology protection expertise.
Enterprise Content Management and Information Governance
Information architecture organizes content logically supporting efficient discovery and reuse. Taxonomy development establishes controlled vocabularies standardizing content classification. Content migration transfers information from legacy systems to modern platforms. Integration with business applications embeds content management into operational workflows. Access controls protect sensitive content while enabling collaboration among authorized users. Audit trails document content access and modifications supporting compliance verification. E-discovery capabilities support legal proceedings requiring comprehensive content search and preservation. Content analytics provide insights into usage patterns and content effectiveness. Content management professionals benefit from information storage certifications validating platform expertise.
Cloud Infrastructure and Information Management
Data lakes aggregate raw data from diverse sources enabling comprehensive analytics. Data warehouses structure information for business intelligence and reporting. Data pipelines orchestrate extraction, transformation, and loading workflows. Data governance establishes quality standards, access controls, and compliance procedures. Data catalog services provide metadata management and discovery capabilities across distributed data estates. Data classification identifies sensitive information requiring enhanced protection. Data lifecycle management automatically transitions less-frequently accessed data to lower-cost storage tiers. Disaster recovery capabilities protect against data loss through backup and replication. Cloud information professionals benefit from cloud infrastructure certifications demonstrating platform management expertise.
Conclusion:
Established foundational competencies spanning visual design, interaction patterns, responsive implementation, collaboration practices, prototyping workflows, accessibility, performance optimization, content strategy, design systems, data visualization, career progression, file management, security awareness, professional development, networking fundamentals, intrusion prevention, cloud platforms, container orchestration, Microsoft certifications, and project selection. These diverse skills collectively define modern web design practice where professionals must balance creative expression with technical constraints, user needs with business objectives, and innovation with accessibility. The breadth of required knowledge reflects how web design has evolved from isolated graphic design activity into integrated discipline touching virtually every aspect of digital product development.
How web design principles adapt across enterprise software, healthcare, e-commerce, education, financial services, government, media, travel, non-profit, real estate, recruitment, gaming, automotive, insurance, and social networking domains. Each industry brings unique requirements, regulations, user expectations, and success metrics that designers must understand and address. Healthcare demands HIPAA compliance and patient safety considerations. E-commerce prioritizes conversion optimization and trust building. Government requires accessibility and multilingual support serving diverse populations. Financial services emphasize security and real-time data presentation. These domain-specific considerations prevent one-size-fits-all design approaches, requiring designers to research industry contexts, understand domain terminology, and appreciate specialized workflows.
Network defense, application penetration testing, wireless security, cloud security architecture, executive security leadership, enterprise risk management, digital forensics, security analysis, security specialist roles, industrial control systems, content management, and cloud infrastructure. These advanced topics demonstrate career pathways available to designers who deepen technical expertise or transition into adjacent disciplines leveraging foundational design knowledge. Security-conscious design becomes increasingly critical as threats evolve and regulations mandate protective controls. Forensic capabilities support incident investigation when security measures fail. Cloud platforms dominate modern infrastructure requiring designers to understand deployment models and service constraints.
The integration of these diverse topics reveals several fundamental truths about contemporary web design extending beyond specific techniques or tools. First, user-centered design remains paramount regardless of domain or specialization, with successful designers maintaining focus on user needs, behaviors, and contexts throughout design processes. Second, accessibility represents ethical imperative and legal requirement rather than optional enhancement, demanding inclusive design practices from project inception. Third, performance directly impacts user satisfaction and business outcomes, making optimization a core design responsibility rather than purely technical concern. Fourth, security permeates all design decisions from authentication interfaces through data display, requiring security awareness throughout design processes.
Collaboration emerges as a consistent theme given the complexity of modern web projects involving designers, developers, product managers, content strategists, marketing professionals, and executive stakeholders. Designers must communicate effectively across disciplines, translate business requirements into design solutions, justify design decisions through research and testing, and incorporate feedback constructively. Remote work and distributed teams introduce additional collaboration challenges requiring mastery of digital communication tools and asynchronous workflows. Design systems and component libraries facilitate collaboration by establishing shared languages and reusable patterns reducing duplicate effort while ensuring consistency.
Looking toward future developments, web design continues evolving as new technologies emerge and user expectations shift. Artificial intelligence integration enables personalization at scale, predictive interfaces anticipating user needs, and automated design assistance generating layout variations or content suggestions. Voice interfaces and conversational UI expand interaction modalities beyond visual displays and touch inputs. Augmented reality and virtual reality create immersive experiences blurring boundaries between physical and digital environments. Progressive web applications combine web’s reach with native application capabilities including offline functionality and device integration. Blockchain technologies enable decentralized applications with novel trust and ownership models.

